Article Title :
Gender, Territory and Entrepreneurship Among Unemployed Graduates in Physical Activities and Sports: The Case of Tunisia 
5 (2021)
59-70
Attitude , Entrepreneurship , Gender , Sports , Social Norms , Unemployment


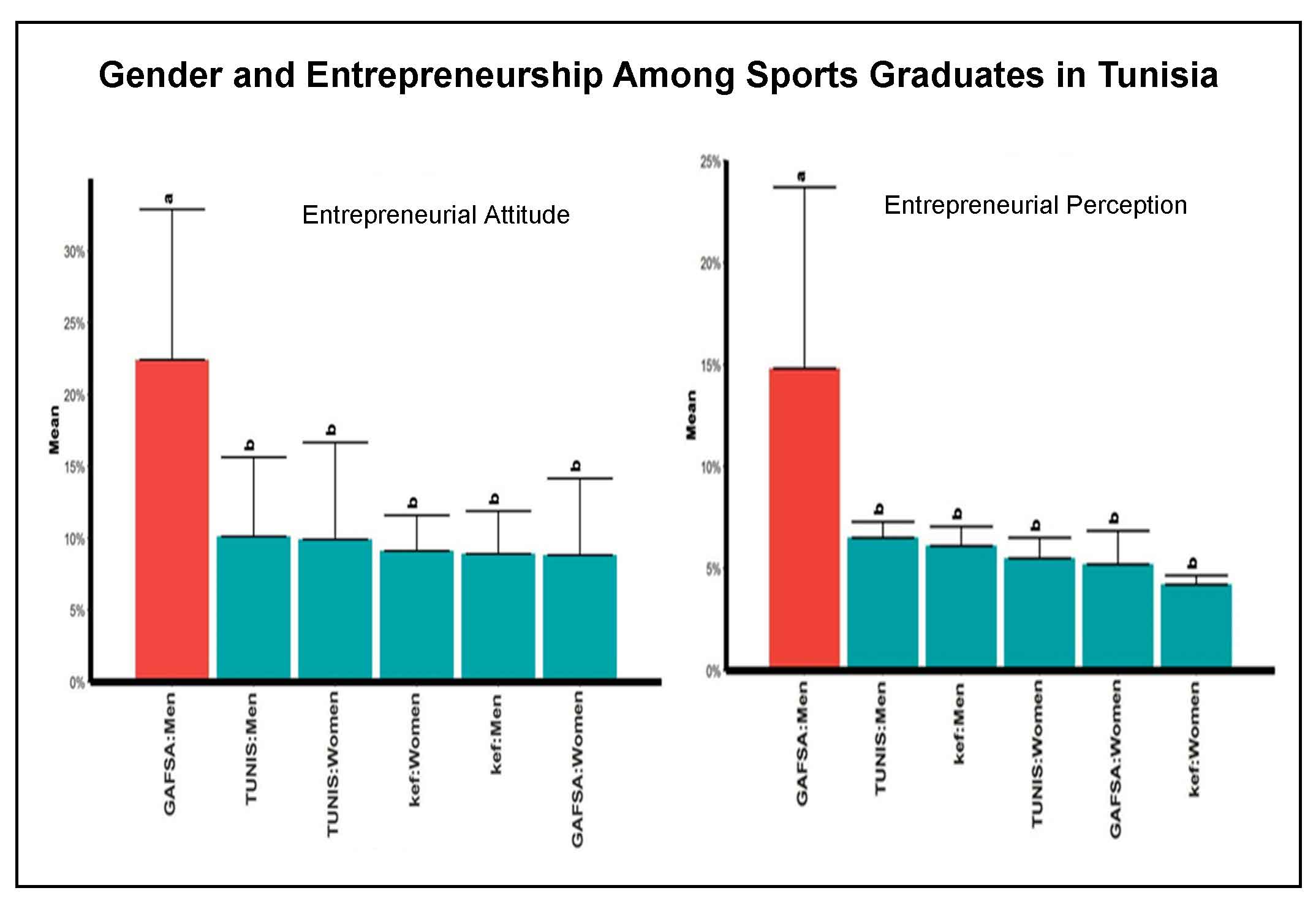
Nationally, Tunisia is not entrepreneurial. It shows a deficit in the creation of innovative businesses. At the regional level, the revitalization of disadvantaged regions facing a problem of underemployment, in particular of highly educated graduates, is justified by the revitalizing entrepreneurial behavior in these areas. This observation is also valid in the sports sector, where unemployment has reached 100% since 2011. Because of this system crisis, which has broken out in Tunisia, we propose in what follows to consider the aspects relating to regional deficiencies by gender, in terms of sports entrepreneurship. The objective of this study is to identify the outlines of a regional catching-up strategy, so that the creation of a ludo-sports project is a challenge that graduates of stapsistes should take up that graduates of stapsistes should take up, pertaining the spirit of equity between the two sexes. This equality is not only desired for an objective of social justice, but also as an essential condition for complementarity and healthy economic development. The results of this quantitative study with 300 unemployed stapsistes belonging to three regions of Tunisia (Kef, Grand Tunis and Gafsa), revealed a favorable entrepreneurial behaviour towards a very favorable entrepreneurial reaction towards the creation of project and a positive correlation between gender, territory and entrepreneurship factors. However, only the Gafsois group seems to be different from the other groups, as it shows a very strong correlation, explained in particular by the socio-cultural factors related to the region.
The unemployment in sports sector reached 100% since 2011.
The study was focused identify the outlines of a regional catching-up strategy for creation of a ludo-sports project pertaining the spirit of equity between the two sexes.
The quantitative study conducted with 300 unemployed stapsistes belonging to three regions of Tunisia (Kef, Grand Tunis and Gafsa).
The study revealed a favorable entrepreneurial behaviour towards a very favorable entrepreneurial reaction towards the creation of project and a positive correlation between gender, territory and entrepreneurship factors.
Ahmed, I., Nawaz, M. M., Ahmad, Z., Shaukat, M. Z., Usman, A., Rehman W. and Ahmed, N., 2010. Determinents of students, entrepreneurial career intentions : Evidence from business graduates. European Journal of Social Sciences, 15 (2), 14-22.
Ajzen, I., 1991. Theory of planned behavior. Organizationna lBehavorIour And Human Decision Processes, 50, 179-211.
Anne F., 1992. La mesure de l’efficacité du sponsoring. Revue Française de Marketing, 138(3), 123-136.
Audet, J., 2003. L’intention de créer sa propre entreprise: Un désir bien ancré en soi ou un état d’âme passager? Conférence de l’Association des Sciences Administratives du Canada (ASAC), Halifax, Canada.
Ben Slama M., 2011. Entrepreneuriat, DeveloppementRegional Et Emploi. Centre Tunisien d’Etudes Economiques, Institut Arabe Des Chefs d’Entreprises, Tunisie.
Bernard, M. J., 2006. La résilience entrepreneuriale. Cahiers de recherché, EMLYON Business School, (05).
Bhattacharjee, A., J., Bonnet, N. Le Pape, A. and Renault, R., 2008. Entrepreneurial motives and performance: Why might better educated entrepreneurs be less successful? Cergy-Pontoise: Working Paper du THEMA, Université de Cergy-Pontoise.
Bonnet, J., 2007. La Dynamique Entrepreneuriale Du (Des) Territoire (S) Français : Entre Firmes Entrepreneuriales Et Entrepreneuriat Lié à L’économie Résidentielle.CJRS (Online)/ RCSR (en ligne) 33, Spécial Issue/Numéro spécial, 27-38 27.
CNFCE [Chambre Nationale des Femmes Chefs d’Entreprises], 2010. Femmes chefs d’entreprises : Bilan et perspectives, Tunis, In Organisation Internationale de Travail (2006). Evaluation nationale du développement de l’entrepreneurial féminin: Tunisie. Organisation Internationale du Travail, Equipe d’appui technique de l’OIT au travail décent pour l’Afrique du Nord et bureau de pays de l’OIT pour l’Egypte et l’Erythrée, Le Caire: OIT.
Davezies, L., 2008. La république et ses territoires, la circulation invisible des richesses. Paris: La République des idées, Éditions du Seuil.
Defélix, C. and Mazzilli, I., 2009. De l'individu au territoire : la longue marche de la gestion des compétences. In D. Retour, T. Picq, C. Defélix, 2009. Gestion des compétences. Nouvelles dimensions, nouvelles relations, Paris, Vuibert, 197-209.
Defélix, C., Culié, J.-D., Retour, D. and Valette, A., 2006. Les pôles de compétitivité, laboratoire d’innovation en ressources humaines? Revue Française de Gestion Industrielle, (25), 3, 69-86.
Defélix, C., Degruel, M., Le Boulaire, M. and Retour D., 2010. Territorialisation de la GRH : de nouvelles démarches d’entreprise et une nouvelle GRH ? 21ème Congrès de l’AGRH, Rennes/St-Malo, 20, 366.
Fagnoni, E., 2014. Faire patrimoine et Faire territoire: l’exemple du Bassin minier uni/UNESCO. B.Gravari and S.Jacquot (Dir), Patrimoine mondial et développement : au défi du tourisme durable.Presses de l’Université du Québec, 79- 103.
Fairlie, R. W. and Robb, A., 2006. Families, Human Capital and Small Business: Evidence from the Characteristics of Business Owners Survey dans Prof. Dr. Mirjaam van Praag (dir.), Entrepreneurship and Human Capital. Amsterdam, ACE (Amsterdam Center for Entrepreneurship), Juillet, 7-13.
Fitouri, C. H., 2019. Genre et Intention Entrepreneuriale chez les étudiants de l’ISSEP. La pratique sportive à l‘épreuve du genre. Série Recherches, Université De La Manouba, 81-91.
Huberty, C. J. and Olejnik, S., 2006. Applied MANOVA and discriminant analysis. Second Edition, John Wiley And Sons, INC. Publication.
INS [Institut National de Statistique], 2014. Recensement nationale de la population tunisienne. Tunisie : rapports analyse genre recensement site-statistique Tunisie.
Institut National de Statistique and la Banque Mondiale, 2016. Carte de la pauvreté en Tunisie. NISet la Banque Mondiale, Tunisie.
La Gazette des Communes, 2006. La politique de cohésion des villes : la contribution des villes et des agglomérations à la croissance et à l’emploi au sein des régions. La Gazette des Communes.
Lazzaretti, L., 2004. Art Cities, Cultural Districts and Museums. Firenze, Firenze University Press.
Moreau, R., 2006. Quelle stabilité pour l’intention entrepreneuriale ? L’internationalisation des PME et ses conséquences sur les stratégies entrepreneuriales. 25, 26, 27 Octobre, Haute Ecole de Gestion Fribourg, Suisse.
Muller, S., 2004. Gender gaps in potentiel for entrepreneurship across countries and cultures. Journal of Developmental Entrepreneurship, 9 (3) 199-220.
Observatoire National du Sport, 2010. Les pratiques physiques et sportives chez les tunisiens, regards croisés. Tunis, Les Editions l’ONS.
Organisation Internationale de Travail, 2006. Evaluation nationale du développement de l’entrepreneurial féminin : Tunisie. Equipe d’appui technique de l’OIT au travail décent pour l’Afrique du Nord, Copyright : Organisation Internationale du Travail, Première édition.
Shapero, A. and Sokol, L., 1982. The social dimensions of entrepreneurship. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign's Academy for Entrepreneurial Leadership Historical Research Reference in Entrepreneurship.
Solidarité Olympique, 2010. Manuel d’administration sportive. The Lowe Martin Group Ottawa, Canada.
Trabelsi, S., 2016. Développement local et valorisation du patrimoine culturel fragile : le rôle médiateur des O.N.G. Cas du Sud-tunisien. Thèse de doctorat, Université Côte d’Azur.
Ucbasaran, D., Westhead, P. and Wright, M., 2006. Opportunity Identification and Pursuit: Does an Eentrepreneur’s Human Capital Matter ? dans Prof. Dr. Mirjaam van Praag(dir.), Entrepreneurship and Human Capital. Amsterdam, ACE (Amsterdam Center for Entrepreneurship), Juillet, 59-64.
Varraut, A., 1998. Démarche stratégique du dirigeant propriétaire de PME. 4ème Congrès International Francophone Sur Le PME, Octobre 1998.