Article Title :
Monsoon Variability Reconstructed from Sedimentological and Mineral Magnetic Studies from Vaghad Tank Deposits, Nashik District, Maharashtra 
5 (2021)
85-100
Sediment Texture , Sedimentology , Monsoon Variability , Magnetic Susceptibility , Grain-size


An attempt made to reconstruct the monsoon variability using sedimentological, geochemical and mineral magnetic studies from deposits in Vaghad Tank, Nashik district, Maharashtra (India). The ~140 years multi-proxy data of the 3.3 meter thick sedimentary section of the tank exhibits some minor changes in sediment characteristics up to the depth of ~150 cm. The grain-size analysis and mineral magnetic studies of 67 samples of sediment suggests that, the sediment dominated by clay. Overall, sedimentary profile does not exhibit any systematic trend in the sediment properties. Finally, the present study concludes no significant changes in the past monsoon conditions have been occurred during the last century but some minor changes in the hydrodynamic conditions have been noticed during the last few decades.
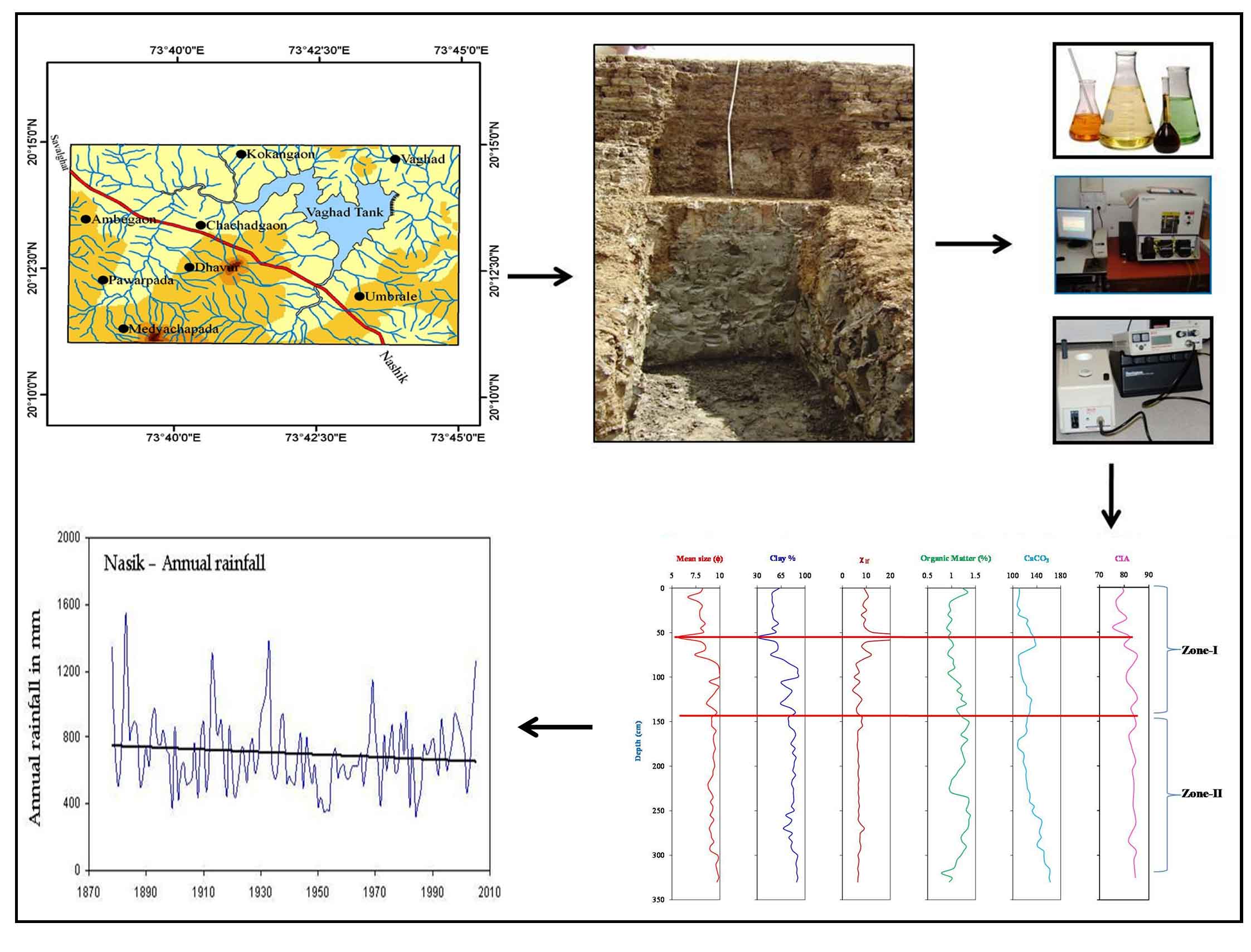
The multi-proxy data about sediments from the tank can provide valuable information on monsoon variability.
Total 67 sediment samples analyzed from 3.3 m thick section to reconstruct the rainfall.
The upper (and younger) sediments show considerable variations in the sediment characteristics.
The past monsoon rainfall conditions are more or less similar during the early few decades.
Abhyankar, H. G., 1987. Late Quaternary palaeoclimatic studies of western India. Unpublished PhD Thesis, submitted to the University of Poona, Pune.
Basavaiah, N. and Khadkikar, A. S., 2004. Environmental magnetism and its application towards palaeomonsoon reconstruction. Journal of Indian Geophysical Union, 8, 1-14.
Brown, A. G., 2003. Global environmental change and the palaeohydrology of Western Europe: A Review. In: Palaeohydrology, Understanding Global Change, K.J Gregory and G. Benito (eds.). John Wiley and Sons Ltd, Chichester, 105-121.
Chauhan, M. S., Mazari, R. K. and Rajagopalan, G., 2000. Vegetation and climate in upper Spiti region, Himachal Pradesh during late Holocene. Current Science, 79, 373-377.
Collinson, J. D. and Thompson, D. B., 1989. Sedimentary structures. Unwin Hyman Ltd, London, 2.
Gazetteer of the Nashik District, 1975. Gazetteers Department, Government of Maharashtra, Mumbai.
Gupta, A.K. and Thamban, M., 2008. Holocene Indian monsoon variability. Glimpses of Geoscience Research in India, The Indian Report to IUGS 2004-2008, edited by Singhvi, A.K., Bhattacharya, A. and Guha, S., INSA, New Delhi, 28-31.
Kale, V. S., Gupta, A., and Singhvi, A. K., 2003. Late Pleistocene-Holocene Palaeo-hydrology of monsoon Asia. In: Palaeohydrology, Understanding Global Change. K.J Gregory and G. Benito (Eds.). John Wiley and Sons Ltd, Chichester, 213-232.
Munsell Color, 1975. Munsell Soil Color Charts. Macbeth Division, Kollmorgen Corporation, Baltimore, Maryland., USA.
Operator’s Manual, 2018. SediGraph III 5120, Micromeritics Instrument Corporation, 4356 Communications Drive, Norcross, Georgia, United States, 30093.
Pant, R. K., Phadtare, N. R., Chamyal, L.S. and Juyal, N., 2005a. Quaternary deposits in Ladakh and Karokoram Himalaya: A treasure trove of the palaeoclimate records. Current Science, 88, 1789-1798.
Pawar, N. J., Kale, V. S., Atkinson, T. C. and Rowe, R. J., 1988. Early Holocene waterfall tufa from semi-arid Maharashtra plateau (India). Journal Geological Society of India, 32, 513-515.
Pettijohn, F. J., 1975. Sedimentary Rocks. Harper and Row Publishers, New York, 24-26.
Sangode, S. J., Sinha, R., Phartiyal, B., Chauhan, O. S., Mazari, R. K., Bagati, T. N., Suresh, N., Mishra, S., Kumar, R. and Bhattacharjee, P., 2007. Environmental magnetic studies on some quaternary sediments of varied depositional settings in the Indian sub-continent. Quaternary International, 159, 1-134.
Sant, D. A., Krishna, K., Rangarajan, G., Basavaiah, N., Pandya, C., Sharma, M. and Trivedi, Y., 2004. Characterization of flood plain and climate change using multiproxy records from Mahi River Basin, Mainland Gujrat. Journal of Indian Geophysical Union. 8, 39-48.
Shankar, R., Prabhu, C. N., Warrier, A. K., Vijaya Kumar, G. T. and Sekar, B., 2006. A multi-decadal rock magnetic record of monsoonal variations during the past 3,700 years from a tropical Indian tank. Journal Geological Society of India, 68, 447-459.
Sinha, R., Stueben, D. and Berner, Z., 2004. Palaeohydrology of the Sambhar Playa, Thar Desert, India. Journal Geological Society of India, 64, 419-430.