Article Title :
Identification of Groundwater Potential Zones Using AHP, GIS and RS Integration: A Case Study of Didessa Sub-Basin, Western Ethiopia 
6 (2022)
1-15
Ethiopia , Remote Sensing , Ground Water Potential Zone , GIS , AHP


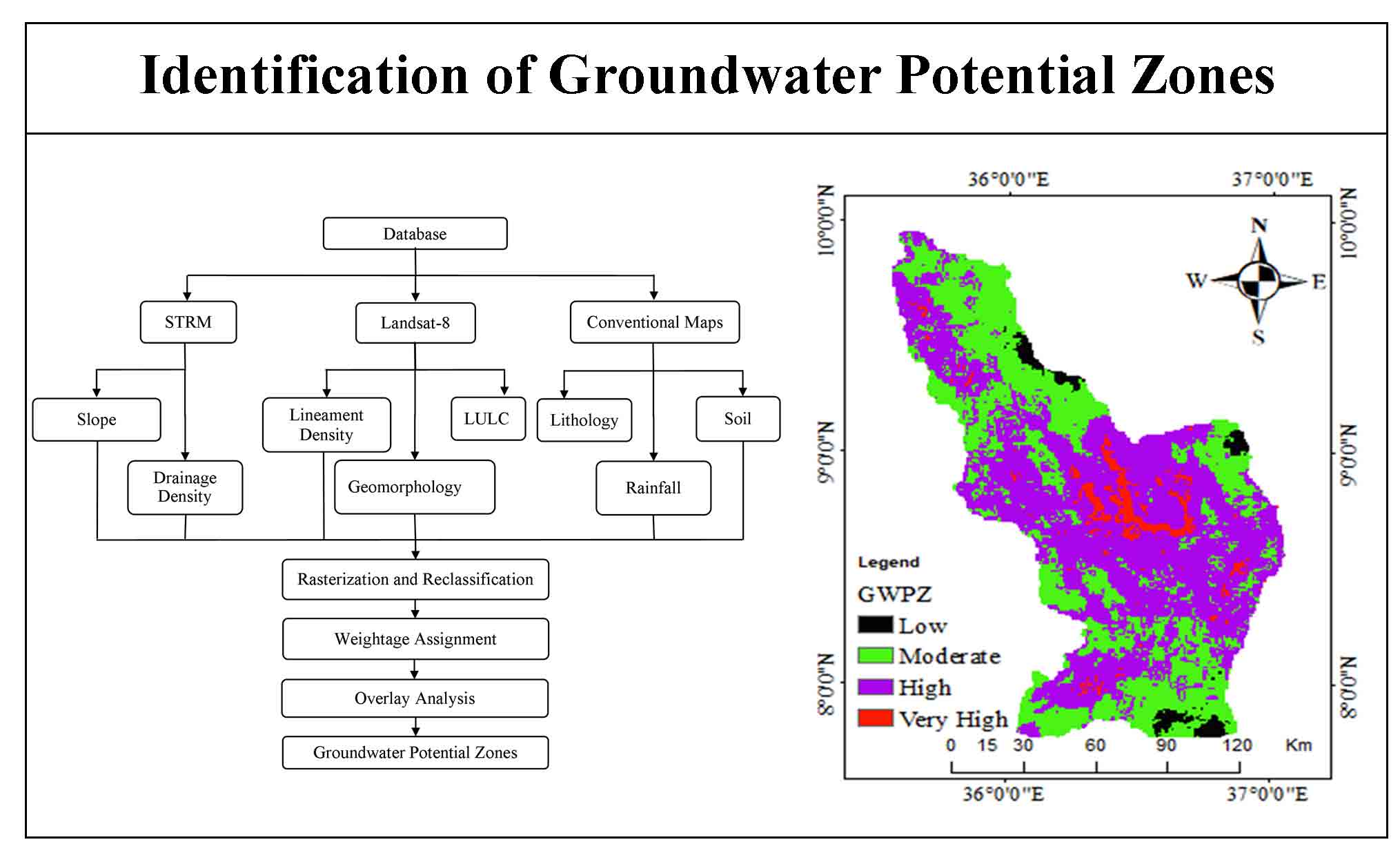
Groundwater is a precious water resource in underground rocks and major water source for drinking, industry and irrigation. Identifying the groundwater potential zones in certain areas of Ethiopia is still challenging in terms of time and cost for resolving water scarcity. Groundwater evaluations in Ethiopia are normally done based on field survey. Therefore, this study aims to use the timely and cost-effective remote sensing data and GIS techniques for the evaluation of groundwater potentials in Didessa Sub-Basin from Western Ethiopia. STRM DEM and Landsat-8 satellite image with secondary data was used for this study. Thematic layers showing distribution of slope, lithology, lineament density, drainage density, LULC, soil texture and rainfall were analyzed using weight overlay analysis and AHP algorithm to determine the groundwater potentials. The weights for each element then assigned according to their relative relevance using Saaty’s (AHP) scale. The rainfall and geomorphology showed a higher weight and lithology the lowest. About 4.6% (1289.4km2) of the study area was classified as ‘very high potential, 66% (18532.2 km2) classified as ‘high potential, 27% (7683km2) as moderate potential and 2.1% (587.5 km2) as ‘low’ groundwater potential areas. Therefore, this study demonstrates a robust method, efficient and useful technique for delineating and mapping groundwater potential zones for planning and decision-making for better groundwater management.
Identifying the groundwater potential zones in certain areas of Ethiopia is still challenging in terms of time and cost for resolving water scarcity problems and the management of groundwater systems.
This study aims to use the timely and cost-effective remote sensing and geographical information system (GIS) techniques for the Evaluation of Groundwater Potential in Didessa Sub-Basin, Western Ethiopia.
Geographical information system (GIS) and remote sensing (RS) are the potential methods to provide all parameters which influence the groundwater potential of one area and it can access, manipulate, and analyze the spatial and temporal data from satellite images.
The delineated Groundwater potential zone was classified into four zones namely, ‘low’, ‘moderate’, ‘high’, and ‘very high’.
The AHP-GIS Remote sensing integrated approach for groundwater potential identification gives an acceptable result.
Abiy, A. Z., Demissie, S. S., MacAlister, C., Dessu., S. B. and Melesse, A. M., 2014. Groundwater Recharge and Contribution to the Tana Sub-basin, Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. In Melesse A., Abtew W. (Eds) Landscape Dynamics, Soils and Hydrological Processes in Varied Climates. Springer Geography. Springer, Cham., 463-481.
Dile, Y. T., Tekleab, S., Bayabil, H. K., Ayana, E. K., Gebrehiwot, S. G., Worqlul, A. W., Srinivasan, R., Yimam, Y. T., Tilahun, S. A, Daggupati, P. and Karlberg, L., 2018. Advances in water resources research in the Upper Blue Nile basin and the way forward: A review. Journal of Hydrology, 560. 407-423.
Kindie, A. T., Enku, T., Moges, M. A. Geremew, B. S. and Atinkut, H. B., 2019. Spatial analysis of groundwater potential using gis based multi criteria decision analysis method in Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia. In Zimale F., Enku Nigussie T., Fanta S. (Eds) Advances of Science and Technology. ICAST 2018. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, 274. Springer, Cham.
Tadesse, N., Nedaw, D., Woldearegay, K., Gebreyohannes, T. and Van Steenbergen, F., 2015. Groundwater management for irrigation in the Raya and Kobo Valleys, Northern Ethiopia. International Journal of Earth Science and Engineering, 8(3), 36-46.
Yifru, B. A., Mitiku, D. B., Tolera, M. B., Chang, S. W. and Chung, Il-M., 2020. Groundwater potential mapping using SWAT and GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis. KSCE Journal of Civil Enineerig. 24, 2546-2559.