Article Title :
Spatial Analysis of Groundwater Qualities in Vempalle Mandal of YSR District, Andhra Pradesh, India using Geospatial Techniques 
Krupavathi Chinthala
,
Srinivasa Gowd Somagouni
,
Ravi Kumar Pappaka
,
Harish Vijay Gudala
,
Pradeep Kumar Badapalli

6 (2022)
1-12
WQI , Water Quality , Spatial Distribution , Groundwater , GIS , Components


The present study analyses the spatial variations of groundwater qualities in the Mogamureru basin of the Vempalle Mandal, YSR district of Andhra Pradesh, South India. Twenty-two groundwater samples from the post-monsoon season collected in January 2020 and tested in the laboratory for chemical analysis including Carbonate (CO3-), Bicarbonate (HCO3-), Magnesium (Mg2+), Chloride (Cl-), Calcium (Ca2+), Sodium (Na+) and Potassium (K+). The spatial variations in quality parameters mapped using interpolation technique in ArcGIS software. Water Quality Index (WQI) calculated for quality analysis and four groundwater samples classified into very poor category and eighteen samples are unsuitable for drinking purpose. The usage of groundwater for drinking purpose needs a proper water quality treatment for better health implications. The methodology adopted in this study has been found to be effective and can be used to establish strong water quality monitoring network in similar areas.
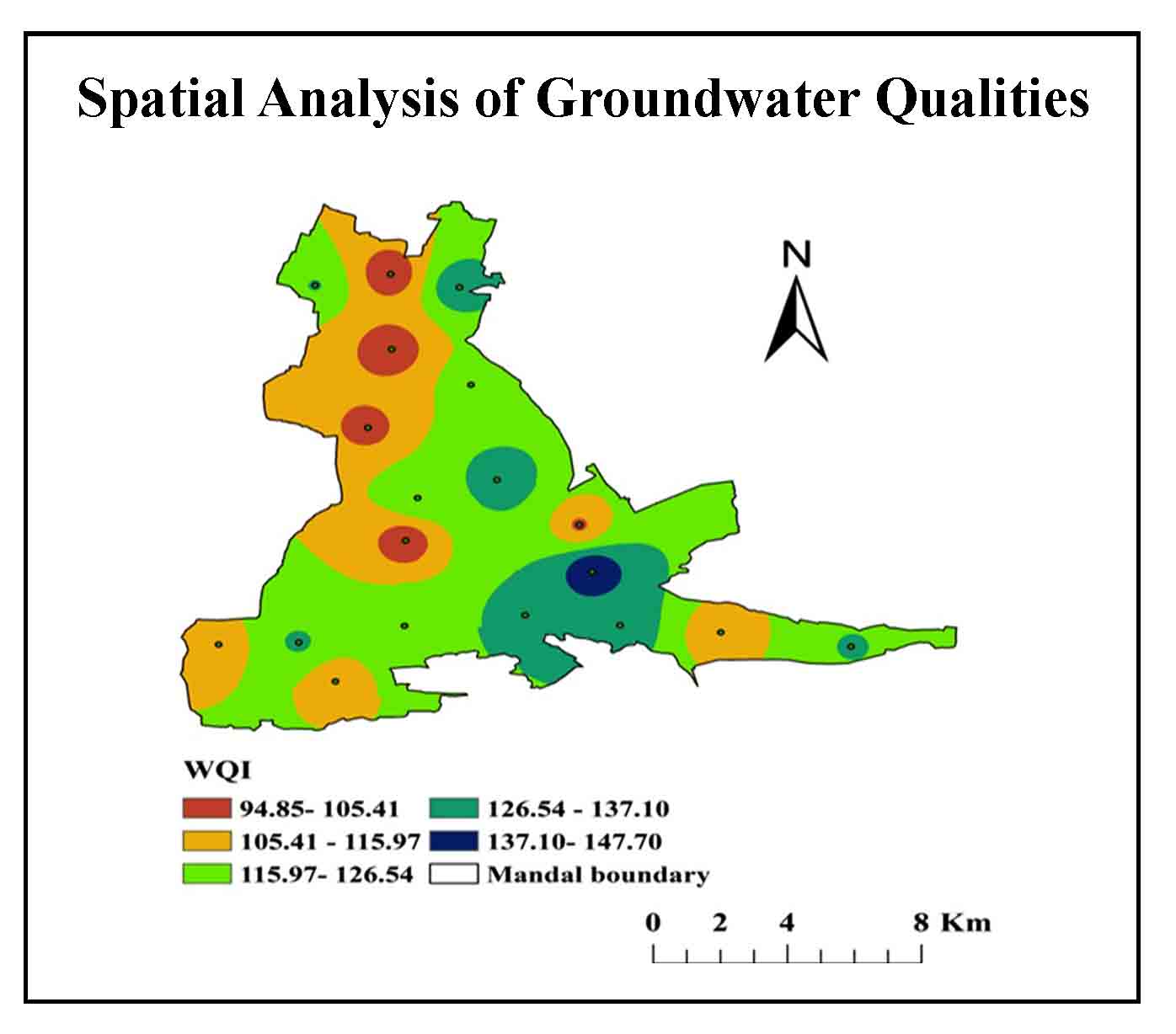
The study focused on analyses of water quality index (WQI) for semi-arid regions of Kadapa, Andhra Pradesh, India.
The acquired water quality index was compered with the BIS and WHO standards.
Four groundwater samples classified into very poor category and eighteen samples are unsuitable for drinking purpose.
The groundwater needs a proper water quality treatment for better human health in the region.
Adimalla, N., 2021. Application of the entropy weighted water quality index (EWQI) and the pollution index of groundwater (PIG) to assess groundwater quality for drinking purposes: A case study in a rural area of Telangana State, India. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 80(1), 31-40.
Balamurugan, P., Shunmugapriya, G. and Vanitha, R., 2020. GIS based assessment of ground water for domestic and irrigation purpose in Vazhapadi Taluk, Salem, Tamil Nadu, India. Taiwan Water Conservancy, 68(2), 1-10.
Bhaskar Rao, Y. J., Pantulu, G. V. C., Reddy, D. V., and Gopalan, K., 1995. Time of early sedimentation and volcanism in the Proterozoic Cuddapah basin, South India: Evidence from Rb-Sr age of Pulivendla mafic sill. Geological Society of India, 33, 329-338.
BIS [Bureau of Indian Standards] 2012. Drinking water - specification (Second revision May 2012), New Delhi.
Brown, R. M., McClelland, N. I., Deininger, R. A. and O’Connor, M.F., 1972. A water quality index- Crashing the psychological barrier. In Indicators Of Environmental Quality, 173-182, Springer, Boston, MA.
CGWB [Central Groundwater Board] 2014. Report on dynamic groundwater resources of India (as on March 2011). Central Groundwater Board, Ministry of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation, Government of India, Faridabad, 1-282.
Chauhan, A. and Singh, S., 2010. Evaluation of Ganga water for drinking purpose by water quality index at Rishikesh, Uttarakhand, India. Report and Opinion, 2(9), 53-61.
Lapworth, D. J., MacDonald, A. M., Kebede, S., Owor, M., Chavula, G., Fallas, H., Wilson, P., Ward, J.S.T., Lark, M., Okullo, Mwathunga, E., Banda, S., Gwengweya, G., Nedaw, D., Jumbo, S., Banks, E., Cook, P. and Casey, V., 2020. Drinking water quality from rural handpump-boreholes in Africa. Environmental Research Letters, 15(6), 064020.
Panneerselvam, B., Muniraj, K., Thomas, M. and Ravichandran, N., 2021. GIS-based legitimatic evaluation of groundwater’s health risk and irrigation susceptibility using water quality index, pollution index, and irrigation indexes in semiarid region. In Groundwater resources development and planning in the semi-arid region, 239-268. Springer, Cham.
Ramaraju, A. and Giridhar, M. V. S. S., 2017. Quality Assessment of Surface Water Bodies in and around GHMC. In National Conference on Water Environment and Society, 322.
Rown, R.M., McCleiland, N.J., Deiniger, R.A. and O’Connor, M.F.A., 1972. Water quality index–crossing the physical barrier. In Proceedings in International Conference on water pollution Research Jerusalem, 6, 787-797.
WHO [World Health Organization] 2017. Global hepatitis report 2017. World Health Organization.