Article Title :
Evaluation of Groundwater Quality for Domestic and Irrigation Suitability from Upper Bhima Basin Western India: A Hydro-geochemical Perspective 
2 (2018)
113-123
Bhima basin , Drinking Water , Groundwater , Hydrogeochemical Analysis , Irrigation , Suitability Analysis , WHO


Major ion constituents present in groundwater are studied for shallow unconfined basaltic aquifer in order to understand the quality of groundwater resources and its impacts on inhabitants and irrigation. 30 groundwater samples collected from dug wells located in upper Bhima basin were analyzed to measure major cations and anions for establishing water quality index (WQI) and irrigation indices. The concentration of pH, electrical conductivity, total hardness, total dissolved solids and major cations and anions were analyzed. Groundwater types were detected using Piper’s trilinear diagram as Ca2+-HCO3−, Ca2+-Na+-HCO3−, mixed Ca2+-Mg2+-Cl− and Ca2+-Cl− groups. High concentration (8 to 194 mg/L) of nitrate was found at some locations in the region. WQI shows 66% of the samples to be unfit for drinking purposes due to high nitrate content mostly introduced because of the anthropogenic activities. Suitability of groundwater for irrigation purposes was determined using of Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR), Permeability Index (PI), Kelly Ratio (KR), Magnesium Hazard (MH), Sodium (%) and Residual Sodium Carbonate (RSC). Groundwater in the region is suitable for irrigation.
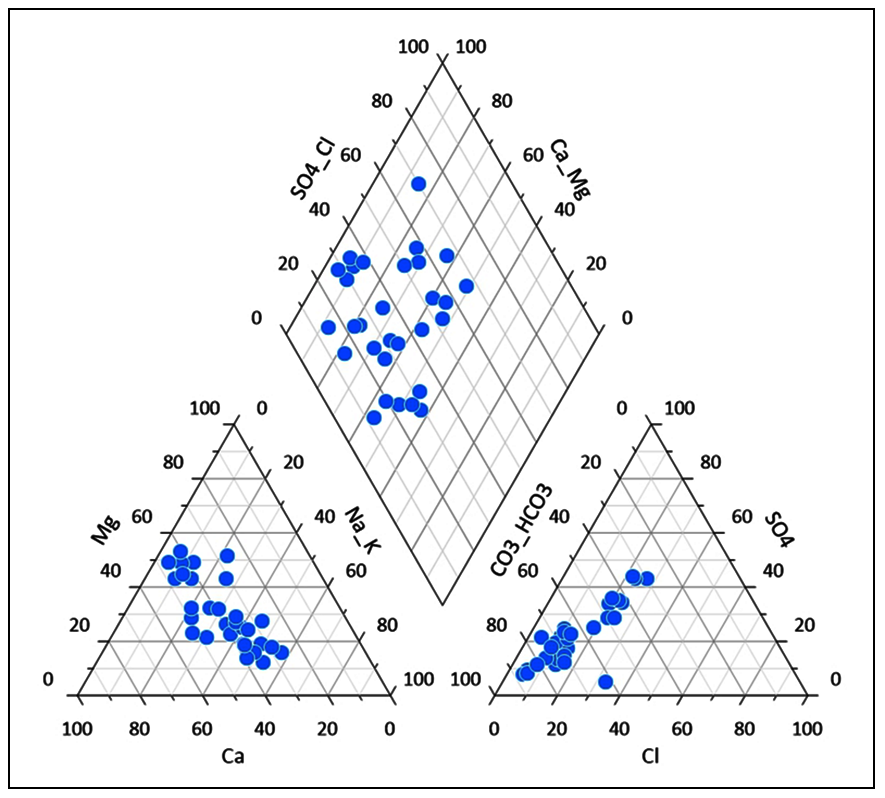
Major ion constituents in groundwater are analyzed for shallow unconfined basaltic aquifer to understand suitability for drinking purpose and irrigation.
Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR), Permeability Index(PI), Kelly’s Ratio (KR), Magnesium Hazard(MH), Sodium Percentage (Na%), Residual Sodium Carbonate(RSC) were detected and estimated for collected groundwater samples from selected wells.
Calculated values were compared with WHO standards and WQI estimated to determine suitability of water for drinking purposes.
About 60% samples show high Nitrate contamination due to intensive agricultural activities and unfit for drinking purposes.
Groundwater in the region is suitable for irrigation and require purification some places.
Deshmukh, K. K., 2011, Assessment of groundwater quality in Sangamner area for sustainable agricultural water use planning. Int. J. Chem. Sci., 9(3), 1486-1500.
Doneen, L. D., 1964. Notes on water quality in agriculture. Published as a water science and engineering paper, 4001, Department of water science and engineering, University of California.
Godbole, .S. M, Rana. R. S. and Natu S. R., 1996. Lava stratigraphy of Western Maharashtra. Gondwana Geol Mag. 2, 125-135.
Hooper. P. R, Subbarao K. V. and Beane. J. E., 1988. The giant plagioclase basalts (GPB) of Western Ghats, Deccan Traps. Mem. Geol. Soc. Ind., 10, 135-140.
Kalpana, L. and Elango, L., 2013. Assessment of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes in Pambar river sub-basin, Tamil Nadu. Environmental protection, 33(1), 1-8.
Kelley, W. P., 1940. Permissible composition and concentration of irrigation waters. In: Proceeding American Society of Civil Engineering, 66, 607-613.
Krishnan, M. S., 1982. Geology of India and Burma, 6th Ed. CBS publisher and distributors, New Delhi.
Piper, M., 1953. A graphic procedure in the geochemical investigation of water analysis. US Geol Surv Groundwater Note, 12, 50-59.
Raghunath, H. M., 1987. Groundwater. New Age International (P) Ltd. Publishers.
Roy, I. and Indranil, 2009. Suitability of GIS and Remote Sensing applications for groundwater management in Sikkim. In Proc. of the Workshop on Integrated Water Resource Management.
Sabale. A. B. and Thorat. P. K., 1991. Geology of parts of Pune and Ahmednagar districts, Maharashtra. Unpublished Progress Report for FS 1989-90.
Todd, D. K., 2006. Groundwater Hydrology. Second Edition Willey- India edition, New Delhi.
USSL [United States Salinity Laboratory], 1954. Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils, handbook 60, US Department of Agriculture, New York.
WHO [World Health Organization], 1993. Guidelines for drinking water quality, 2nd edition, Geneva, 1-3.
Wilcox, L. V., 1955. Classification and use of irrigation waters. U S Department of Agriculture, New York.