Article Title :
Use of Geospatial Techniques for Groundwater Potential Zone Mapping from Phonda Basin in Sindhudurg District Maharashtra: A Geological Influence Approach 
2 (2018)
124-133
Geospatial Techniques , Geology , Groundwater , potential zones , GIS , AHP


The study was conducted to find out the groundwater potential zones (GWPZ) by using geospatial techniques in Phonda basin in Sindhudurg district of Maharashtra (India). Analytical Hierarchical Process (AHP) was used to demarcate the GWPZ using thematic layers: geology, geomorphology, lineament density, drainage density, elevation, slope, soil, rainfall and land use land cove (LULC). The ranks were assigned for each individual parameter of thematic layer and weights assigned to each thematic layer and final groundwater map was prepared by intersection all thematic layers in Arc GIS environment. GWPZs were categorized as: low, moderate, high and very high. Geological factors are influencing groundwater potentials according to geological formations and human activities. Geological influence approach of delineating the GWPZ is useful for planning and monitoring the groundwater resource for sustainable development.
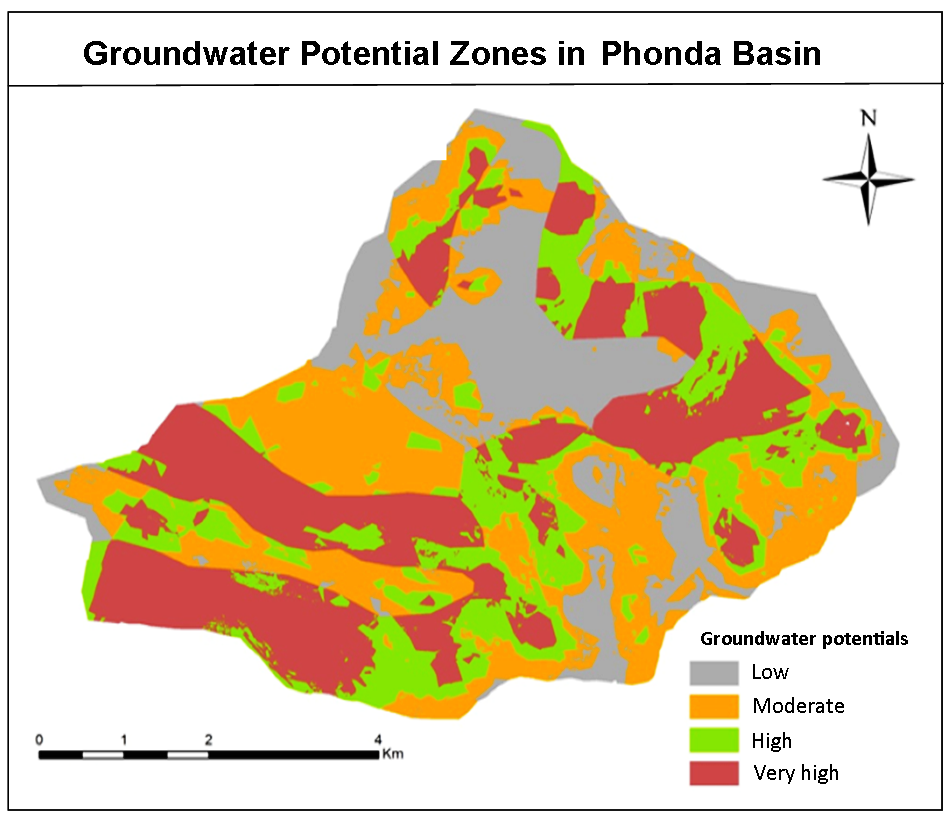
The groundwater potential zones were detected and delineated using AHP and geospatial techniques.
Thematic layers: geology, geomorphology, lineament density, drainage density, elevation, slope, soil, rainfall and land use land cove (LULC) were used for analyses.
The groundwater potential zones were categorized as low, moderate, high and very high.
Very high groundwater potential is estimated in the area with Deccan basalt having vesicular and vertical joints.
Geological influence approach of delineating the GWPZ is useful for planning and monitoring the groundwater resource.
Arkoprovo, B., Adarsa, J. and Prakash, S. S., 2012. Delineation of groundwater potential zones using satellite remote sensing and geographic information system techniques: a case study from Ganjam district, Orissa, India. Research Journal of Recent Sciences, 1(9), 59-66.
GSI [Geological Survey of India], 2001. Geological Survey of India.
Kshirsagar, L. K. and Jadhav, P. B., 2000. Unmetamorphosed precambrian sedimentary sequence (Phonda group) of coastal Maharashtra. In Field Workshop on Integration of the Kaladgi and Bhima Basins (abstract volume), Geological Society of India, Bangalore, 8-10.
Patil, A. and Panhalkar, S. S., 2019. Analytical hierarchy process for landslide hazard zonation of Southwestern Ghats of Maharashtra, India. Disaster advances, 12, 26-33.
Saaty, T. L., 1980. Decision making for leaders: the analytic hierarchy process for decisions in a complex world. 3rd Revised Edition (2013). RWS publications.
Senthil Kumar, G. R. and Shankar, K., 2014. Assessment of groundwater potential zones using GIS. Frontiers in Geosciences, 2(1), 1-10.
Shailaja, G., Kadam, A. K., Gupta, G., Umrikar, B. N. and Pawar, N. J., 2019. Integrated geophysical, geospatial and multiple-criteria decision analysis techniques for delineation of groundwater potential zones in a semi-arid hard-rock aquifer in Maharashtra, India. Hydrogeology Journal, 27(2), 639-654.
Teixeira, J., Chaminé, H. I., Marqus, J. E, Gomes, A., Carvalho. J. M., Albertí, A. P. and Rocha, F. T., 2008. Integrated approach of hydrogeomorphology and GIS mapping to the evaluation of groundwater resources: An example from the hydro mineral system of Caldas Da Cavaca, NW Portugal. Global Groundwater Resource and Management, 227-249.