Article Title :
Identification of Suitable Sites for Artificial Groundwater Recharge Structures in Semi-arid region of Anantapur District: AHP Approach 
Rajasekhar M
 ,
Sudarsana Raju G
,
Imran Basha U
,
Siddi Raju R
,
Pradeep Kumar Badapalli
,
Sudarsana Raju G
,
Imran Basha U
,
Siddi Raju R
,
Pradeep Kumar Badapalli
 ,
Ramachandra M
,
Ramachandra M
3 (2019)
1-11
AHP , Geospatial analysis , GIS , Groundwater , Remote Sensing , Water Conservation , Structure


The conservation and sustainable advancement of soil and water assets is one of the fundamental standards for improvement of arid and semi-arid regions of India. The present study is underway to evaluate the Artificial Groundwater Recharge Zones (AGRZ) in the semi-arid region of Anantapur district, Andhra Pradesh, India using Remote Sensing (RS), Geographical Information System (GIS) and Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) technique. The comparative weights were assigned to different thematic layers with the help of the decision making tool of AHP. A set of eight thematic layers influence groundwater potential (GWP) is determined based on their corresponding weights, which depend on a Saaty’s 9 points scale. These weights are normalized using AHP technique to identify the AGRZs. Five AGRZs were recognized as very low, low, moderate, good and very good, depending on its suitability to identify the sites for groundwater recharge. About 4.29 % (8.96km2) and 17.70 % (36.95km2) area in the region show very good and good potentials of artificial groundwater recharge, respectively. On the other hand 61.59% (128.60km2), 11.94% (24.94km2) and 4.48 % (9.35km2) area showed moderate, poor and very poor potentials. Overall accuracy of AGRZ map is 82.05%. 92 check dams, 19 percolation tanks and 7 check walls were found suitable in the region. The effectiveness and prediction ability of the method depends on integrity of the criterion used. AHP based methodology can be useful for precise and reliable analysis and predictions of groundwater in semi-arid regions of India.
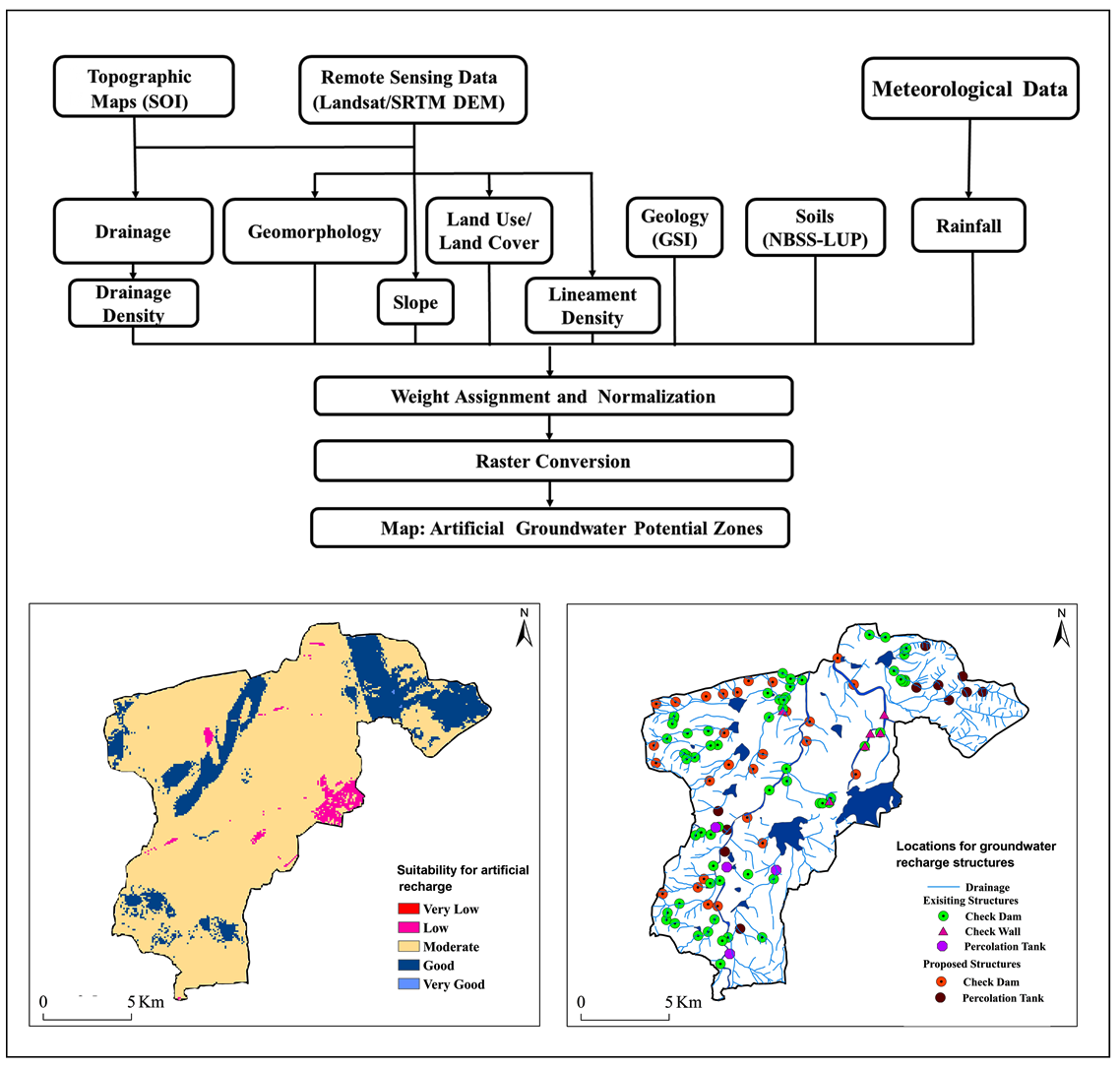
Artificial Groundwater Recharge Zones (AGRZ) in the semi-arid region of Andhra Pradesh, India are identified using RS, GIS and Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) techniques.
The comparative weights were assigned to different thematic layers with the help AHP technique.
These weights were normalized using AHP technique to identify the AGRZs.
Five AGRZs were recognized as very low, low, moderate, good and very good.
About 4.29 % (8.96km2) and 17.70 % (36.95km2) area in the region showed very good and good potentials of artificial groundwater recharge, respectively.
92 check dams, 19 percolation tanks and 7 check walls were found suitable in the region.
CGWB, 2006. Dynamic groundwater resources of Chhattisgarh. Central Groundwater Board, Raipur.
CGWB, 2007. Manual on artificial recharge of groundwater. Central Groundwater Board, New Delhi.
CGWB, 2013a. Master plan for artificial recharge to groundwater in India. Central Groundwater Board, Faridabad.
CGWB, 2013b. Manual on artificial recharge of groundwater. Central Groundwater Board, New Delhi.
Musa, K. A., Akhir, J. M., and Abdullah, I., 2000. Groundwater prediction potential zone in Langat Basin using the integration of remote sensing and GIS. In The 21st Asian Conference on Remote Sensing.
Saaty, T. L., 1980. The analytic hierarchy process: Planning, priority Setting, Resource Allocation. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Saaty, T. L., 1999. Fundamentals of the analytic network process, International Symposium of the Analytic Hierarchy Process (ISAHP), Kobe, Japan.