Article Title :
Site Suitability Analysis for Water Conservation Using AHP and GIS Techniques: A Case Study of Upper Sina River Catchment, Ahmednagar (India) 
3 (2019)
49-59
Analytic Hierarchy Process , GIS , Land Suitability , MCDA , Water Conservation Activity , Water Scarcity


The site suitability for construction of water conservation structures is an important step towards groundwater conservation in arid and semi-arid regions. Water is the most crucial for maintaining an environment and ecosystem which is helpful to sustaining all forms of the life. The increasing water scarcity day to day has been one of the common problems over a period of time. On top of it, when the area is a part of rain shadow zone like Ahmednagar district, water conservation activities are become more important. The present study aims to identify the suitable zones for water conservation activity. Multi- criteria evaluation is carried out using Geographic Information System (GIS) techniques to help the choice makers in defining suitable site for construction of water conservation structures. Different layers which were considered for multi-criteria evaluation: slope, land use land cover, soil texture, lithology, soil depth, soil erosion, wells, lineaments and drainage network. Analytical Hierarchy Processes (AHP) is used for weighted sum to find suitable sites for implementation of water conservation activity using selected criterions. The site suitability map was classified into four classes: highly suitable, moderately suitable, less suitable and not suitable with area of 19.19%, 26%, 49.03% and 5.78, respectively. This map will help for selection of suitable sites for construction of Mati Nala Bund (MNB), Check Dam, Cement Nala Bund (CNB) and Continuous Contour Trenches (CCT) for conservation of groundwater resource in the region.
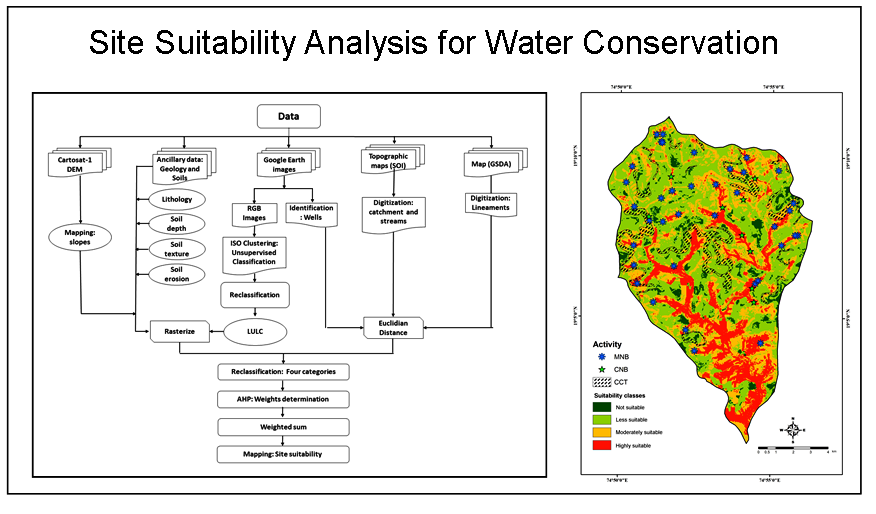
The identification of potential sites for water conservation structure is one of important steps towards successful implementation of the project.
AHP and weighted sum analyses were used for identification of suitable sites for implementation of water conservation activities.
The site suitability map was classified into four classes: highly suitable, moderately suitable, less suitable and not suitable.
The technique used in this study will be useful for planning and monitoring the projects for water conservation in semi-arid regions.
Mukhopadhaya, S., 2016. GIS-based site suitability analysis: case study for professional college in Dehradun. Journal of Civil Engineering and Environmental Technology, 3(1), 60-64.
Saaty, T. L., 1980. The analytic hierarchy process-Planning priority setting resource allocation. McGraw-Hill NY USA [M]. The Analytic Hierarchy Process: Planning, Priority Setting. Resource Allocation.
Varade, A. M., Khare, Y. D., Dongre, K. P., Muley, S. and Wasnik, G., 2017. Integrated geographical information system (GIS)-based decision support system (DSS) approach to identify the sitespecific water conservation structures in a watershed of Nagpur district, Central India. Sustainable Water Resources Management, 3(2), 141-155.