Article Title :
Site Suitability Analysis for Surface Irrigation using GIS, Remote Sensing, and Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) Integration in Wama Watershed, Western Ethiopia 
6 (2022)
40-53
Site Suitability , Remote Sensing , Irrigation , GIS , AHP


The study integrates GIS, Remote Sensing and Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) to evaluate suitable sites for surface irrigation by taking eight parameters into account, including slope, elevation, distance to water source, land use, soil texture, soil type, soil depth, and soil drainage in Wama watershed. A numeric range was created by standardizing each parameter to a single measurement scale, with higher values denoting more suitable and lower values denoting less suitable one. The final site suitability map was prepared in GIS environment by using the weighted overlay method. Distance to streams (44%), slope (18%), elevation (13%), LULC (13%), and soil drainage (5%) scored highly in the pairwise comparison matrix. Additionally, they are the most crucial elements in evaluating eligible lands for surface irrigation, followed by soil depth (4%), soil type (3%), and soil texture (2%). The final suitability map, which will aid in supporting rain-fed agriculture by surface irrigation, was developed with four classifications highly suitable (16%), moderately suitable (49%), marginally suitable (34%), and not suitable (1%). Therefore, this study demonstrates a robust method of using GIS and remote sensing techniques, which is efficient and useful in mapping potential site suitability for surface irrigation and an important guideline for planners, and decision-makers to give the fast decision for irrigation management.
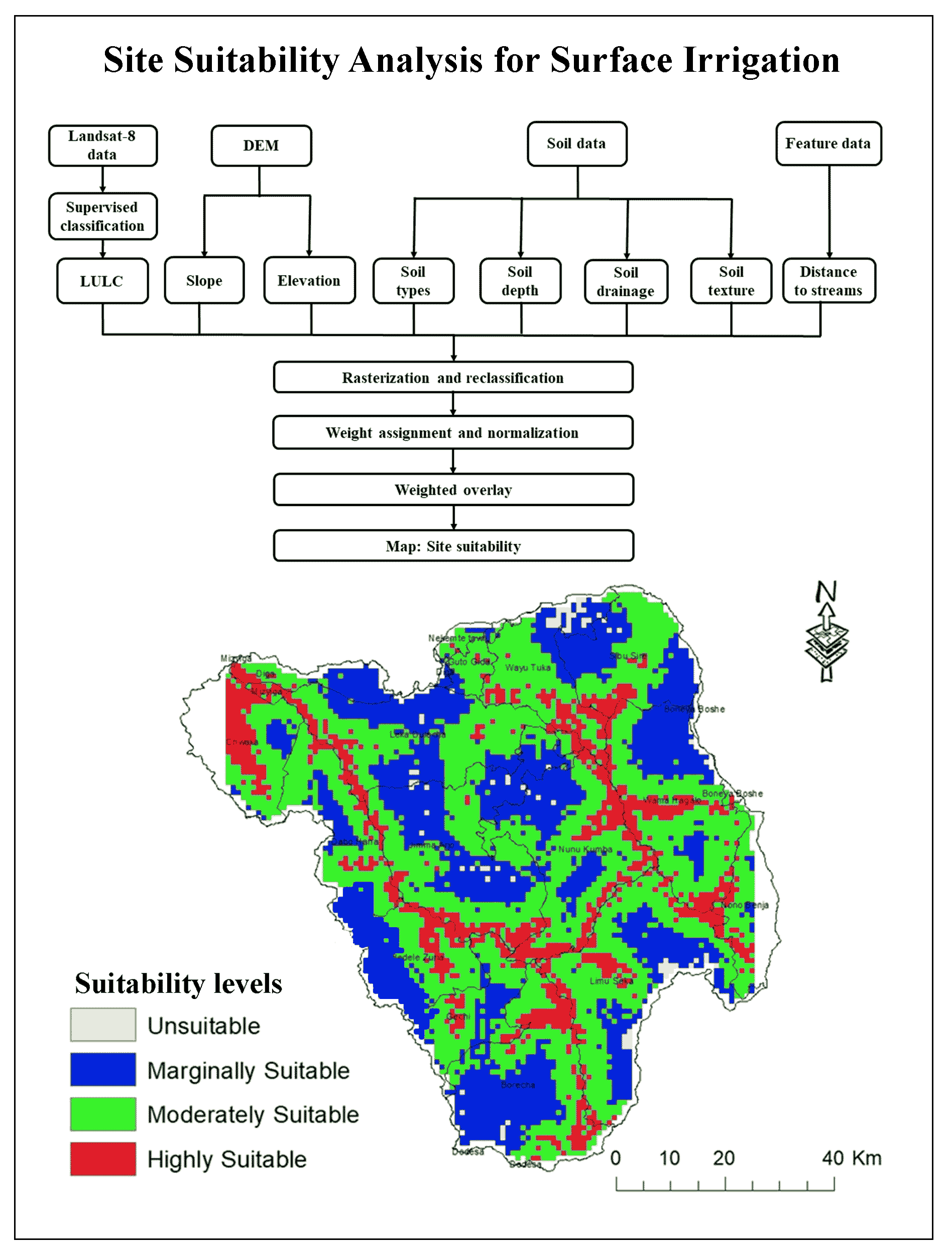
The site suitability analysis is appropriate for irrigation to meet the rising needs of population overreliance on rain fed agriculture.
AHP based multi-criteria analysis is used for site suitability analysis was performed for surface irrigation.
The estiamted suitability map was classified into highly suitable (16%), moderately suitable (49%), marginally suitable (34%), and not suitable (1%).
This is efficient and useful method of mapping the potential site suitability for surface irrigation and an important guideline for planners and decision-makers.
Aybehon, E. Y. and Tiku, A. A., 2022. Land suitability evaluation for surface irrigation using ARC GIS and AHP techniques in Bedessa, Ethiopia. 1st International Online Conference on Agriculture - Advances in Agricultural Science and Technology session Agricultural Water Management, 1-15.
FAO [Food and Agriculture Organization], 1985. Guideline for Land Evaluation for Irrigated Agriculture. Soils Bulletin. FAO, Rome., 55.
FAO [Food and Agriculture Organization], 1985. Guideline for Land Evaluation for Irrigated Agriculture. Soils Bulletin. FAO, Rome., 55.
Saaty, T. L., 1980. The analytic hierarchy process. McGraw-Hill, New York, 5.
World Bank, 2006. Ethiopia: Managing water resources to maximize sustainable growth. Washington DC, USA: A World Bank Water Resources Assistance Strategy for Ethiopia.