Article Title :
Identification of Preferable Ecotourism Destinations in Purulia District, West Bengal (India): AHP and GIS Approach 
6 (2022)
73-93
Suitability , Purulia , GIS , ecotourism , AHP


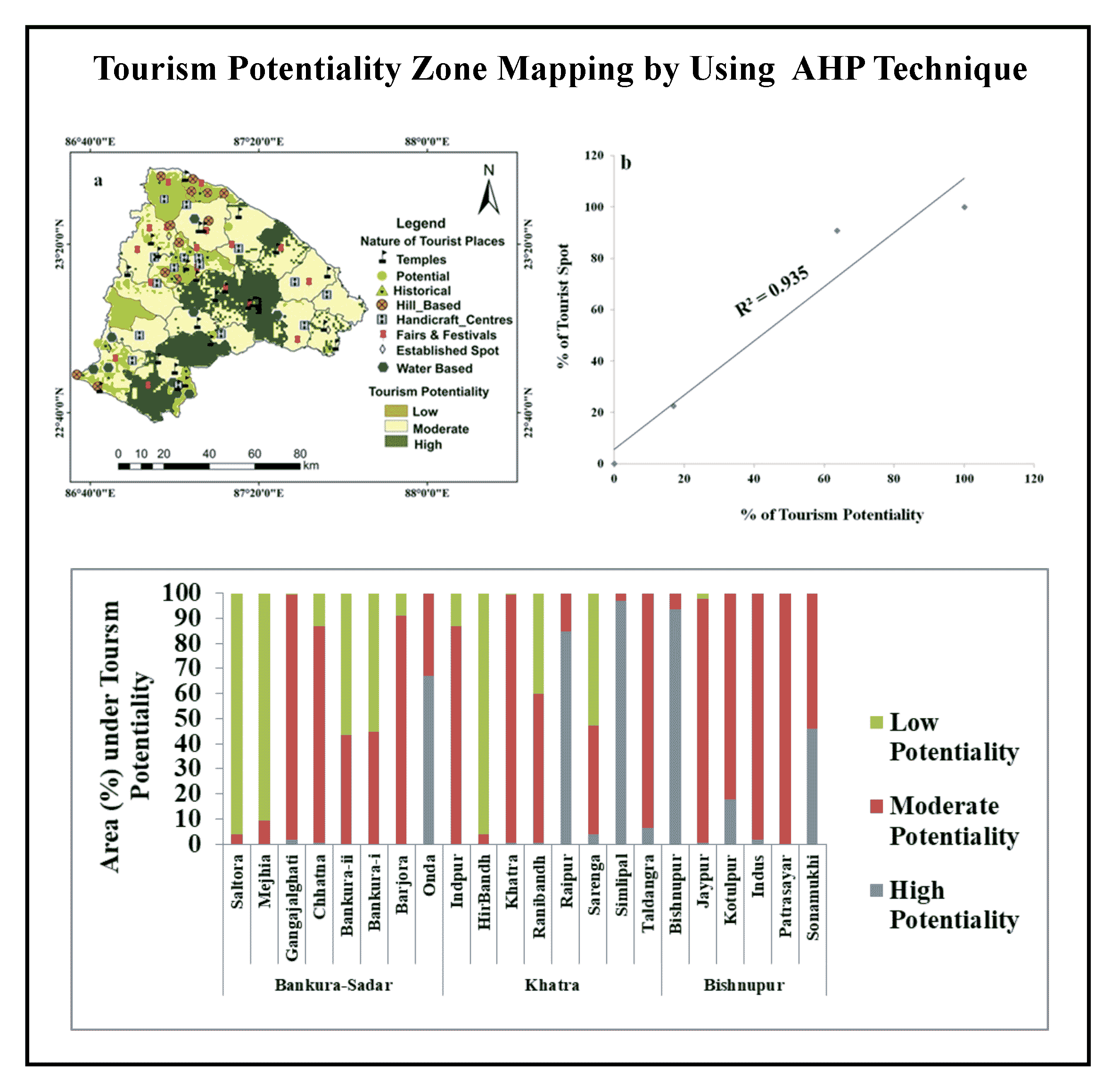
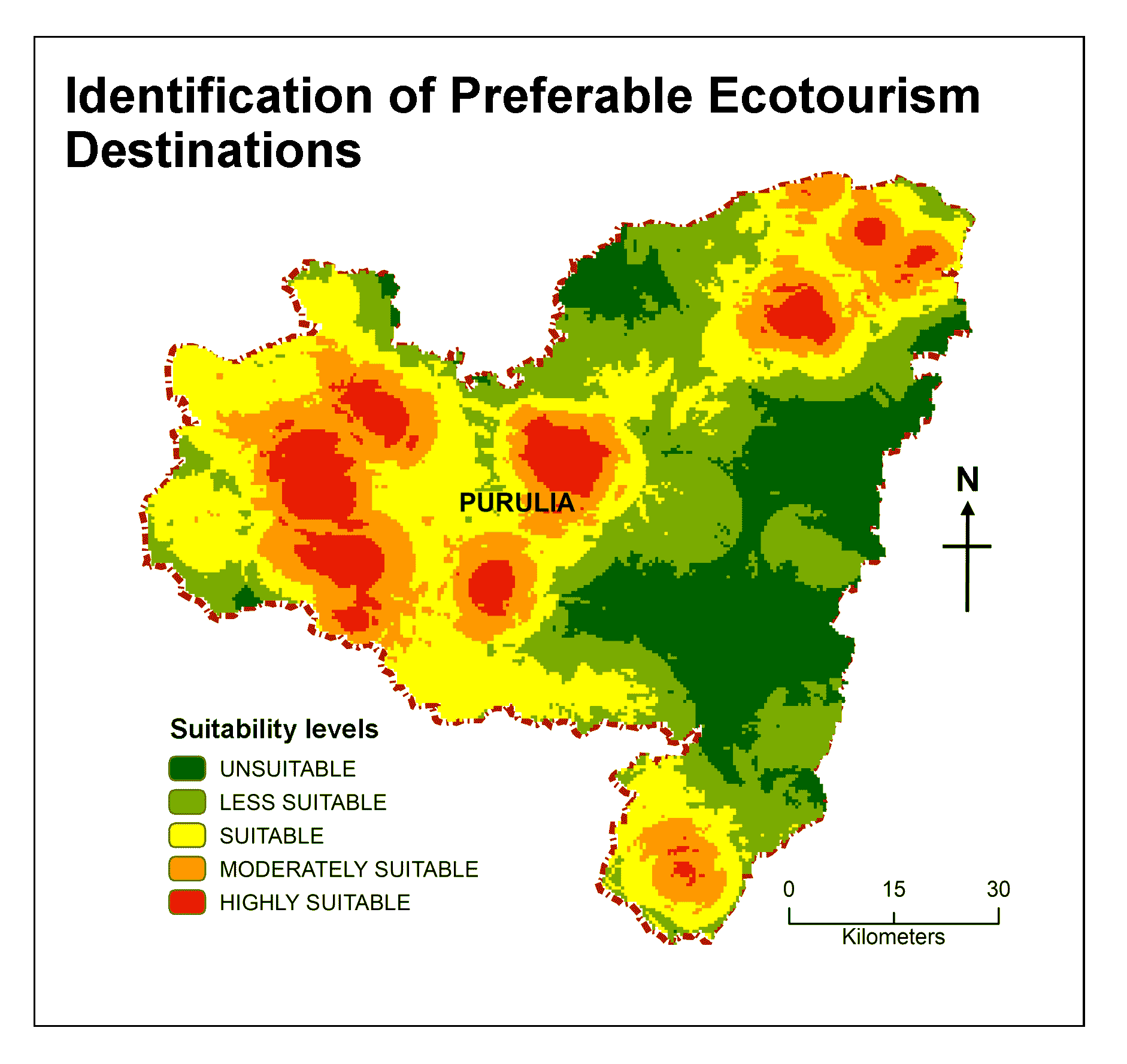
Ecotourism has gained popularity among travelers in recent years due to the detrimental effects of conventional tourism. Purulia district in West Bengal (India), with its diversified picturesque landscape such as lush green forest, mesmerizing riverscape, lakes, waterfall, hills and uniqueness in the local community’s culture gives ample potentiality of ecotourism development. The aim of this paper to explore potentiality of ecotourism in Purulia district, West Bengal, India using Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) and Geographical Information System (GIS). Initially, ecotourism inventory dataset was developed based on following criteria: Elevation, slope, proximity to river, distance from road, distance from settlements, distance from ecological sites, distance from railway, distance from tourism sites using ARC-GIS 10.6.1 software. Later, the suitability map of ecotourism development has been developed by applying Weighted Linear Combination (WLC) with combination of the criteria with their respective weights and categorized into five suitability classes as highly suitable (S1), moderately suitable (S2), suitable (S3), less suitable (S4) and unsuitable (S5). Finally, after the identification of suitable zones, six alternatives ecotourism destinations are identified. This proposed method may be helpful for the local stakeholders and public administration in identifying potential ecotourism destination and planning for sustainable ecotourism development.
The conventional way of tourism harmed the environment by destructing nature and natural landscape.
Purulia district shows diversified picturesque landscape such as lush green forest, mesmerizing riverscape, lakes, waterfall, etc.
This paper explores the potentiality of ecotourism in the Purulia district using AHP and GIS.
The suitability map of ecotourism developed and categorized into five suitability classes: highly suitable, moderately suitable, suitable, less suitable and unsuitable.
This study may be helpful for the policymaker and public administration for planning sustainable eco-tourism development.
Bhattacharyya, D. and Chakraborty, P., 1997. The saraks study of a little known community in Purulia West Bengal, 1-22, Department of Anthropology, University of Burdwan.
Dashti, S., Masoud, M., Hosseini, S. M., Riazi, B. and Momeni, M., 2013. Application of GIS, AHP, fuzzy and WLC in island ecotourism development- Case study of Qeshm Island, Iran. Life Sci J. 10, 1274-1282.
Geremew, Y. M. and Hailemeriam, L. Y., 2015. Site suitability evaluation of ecotourism potentials for sustainable natural resource management and community-based ecotourism development. The case of Bench Maji Zone, south Western part of Ethiopia. Scholars Journal of Arts, Humanities and Social Sciences, 3(8B), 1368-1383.
Ghamgosar, M., 2011. Multicriteria decision making based on analytical hierarchy process (AHP) in GIS for tourism. Middle-East. Journal of Scientific Research, 10(4), 501-507.
Han, W. J. and Tsay, W. D., 1998. Formulation of quality strategy using analytic hierarchy process, twenty seven annual meeting of the Western Decision Science Institute, University of Northern Colorado, USA, 580-583.
Kim, H., Chung, Y., Nishii, K. and Jung, B. D., 2011. The effect of accessibility improvement on tourist excursion behaviors. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 15(8), 1443-1448.
Önder, E., Yıldırım, B. and Özdemir, M., 2013. Multi criteria decision making approach for evaluating tourism destinations in Turkey. Academic Journal of Tourism and Management Researches, 1(1), 1-15.
Prideaux, B. and Cooper, M. (Eds.) 2009. River tourism. Wallingford: CAB International.
Saaty, T. L., 1980. The analytic hierarchy process: Planning, priority setting, resource allocation. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Singh, V., 2015. Eco-Tourism as a Sustainable Alternative to Conventional Tourism. J. Tourism Hospit, 4,168.
Sunlu, U. 2003. Environmental impacts of tourism. Environ. Agric. Mediterr. Reg. Bari CIHEAM 2003, 270, 263-270.
Suryabhagavan, K., Tamirat, H. and Balakrishnan, M., 2015. Multi-criteria evaluation in identification of potential ecotourism sites in Hawassa town and its surroundings, Ethiopia. Journal of Geomatics, 9, 86-92.
Taye, B., Gebre, S. L., Gemeda, D. O. and Getahun, K., 2019. Using geospatial techniques in the selection of potential ecotourism sites in Menz-geramidir district, Ethiopia. Ghana Journal of Geography, 11(1), 201-227.
WTOILO [World Tourism Organization and International Labour Organization], 2013. Economic Crisis, International Tourism Decline and its Impact on the Poor, UNWTO, Madrid.
Zhang, Z., Liu, X. and Yang, S., 2009. A note on the 1-9 scale and index scale in AHP. In Y. Shi, S. Wang, Y. Peng, J. Li and Y. Zeng (Eds.), Cutting-edge research topics on multiple criteria decision making. MCDM 2009. Communications in Computer and Information Science, 35, Berlin: Springer.