Article Title :
Effect of Wastewater on the Soil and Irrigation Process: A Laboratory Study 
1 (2017)
46-55
Heavy Metals , Daily Metal Intake , Enrichment factor , Wastewater


Most of the industrial sewage effluents used for irrigation contains heavy metals which cause toxicity to crop plants as the soils are able to accumulate heavy metal for many years. The vegetables grown for the present study were irrigated with treated wastewater brought from a nearby full-scale sewage treatment plant at different compositions along with tap water as a control. The concentration levels of the Cd, Co, Cu, Mn and Zn in the soil were found to below the toxic limits as prescribed in literature. Daily Intake Metals (DIM) values suggest that the consumption of plants grown in treated wastewater and tap water is nearly free of risks, as the dietary intake limits of Cu, Fe, Zn and Mn. The Enrichment Factor for the treated wastewater irrigated soil was found in order Zn> Ni> Pb> Cr> Cu> Co> Mn> Cd. Thus, treated wastewater can be effectively used for irrigation. This will have twofold significant environmental advantages: (1) helpful to reduce the groundwater usage for irrigation and (2) helpful to reduce the stress on surface water resources.
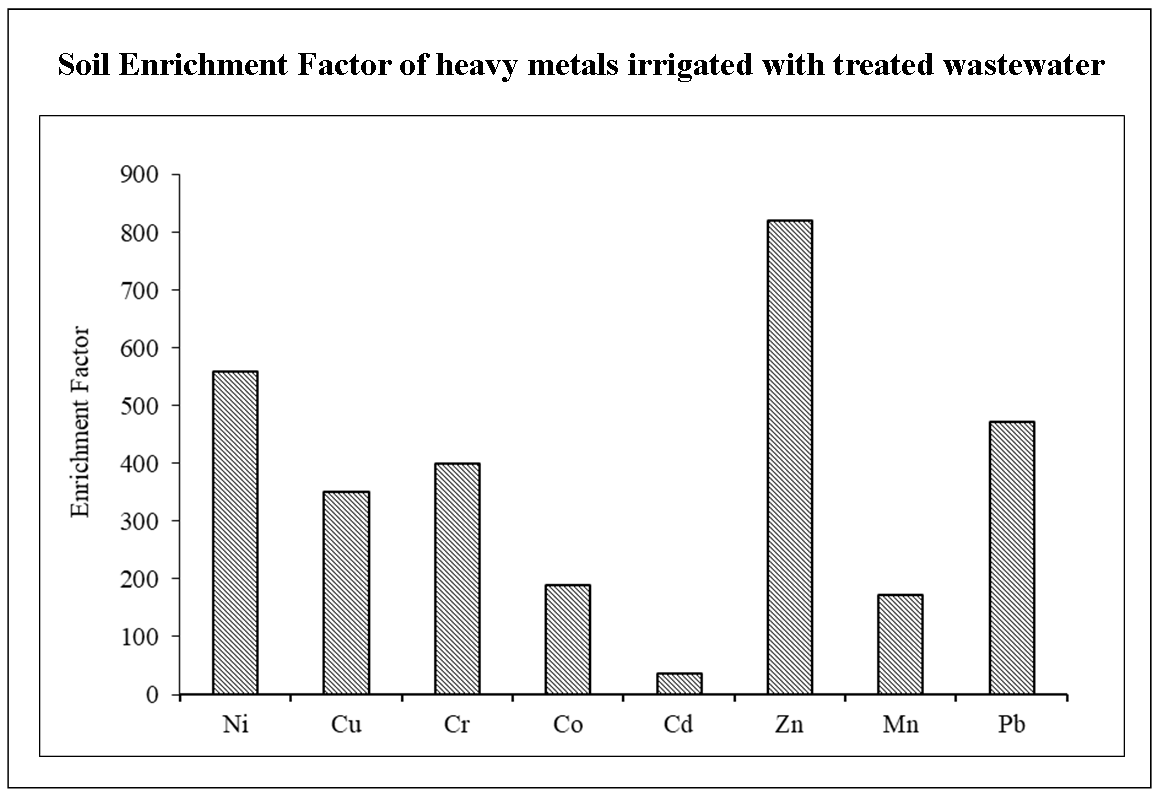
Concentration of the Cd, Co, Cu, Mn and Zn in the soil was found to below the toxic limits.
Soil and plant growth in wastewater is free from risk.
Water used for irrigation can be replaced by wastewater containing these heavy metals.
Soil enrichment factor is maximum value for Zn and minimum value for Cd.
Alrawiq, N., Khairiah., Talib, M. L., Ismail, B.S. and Anizan, I., 2014. Accumulation and translocation of heavy metals in soil and paddy plant samples collected from rice fields irrigated with recycled and non-recycled water in MADA Kedah, Malaysia. International Journal of Chem Tech Research, 6(4), 2347-2356.
APHA [American Public Health Association], 2005. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 21st ed. American Public Health Association, Washington DC, 1220.
Jones, C. and Jacobsen, J., 2003. Nutrient management module, 7. Testing and fertilizer recommendations.
McGrath, S.P., 2001. How organisms live with heavy metals in the environment, Fact sheet on environmental risk assessment, International Council on Metals and the Environment, Ottowa, Canada.
Naz, H., Naz, A. and Ashraf, S., 2015. Impact of heavy metal toxicity to plant growth and nodulation in Chickpea grown under heavy metal stress. International Journal for Research in Emerging Science and technology, 2(5), 248-260.
Panse, V.G. and Sukhatme, P.V., 1985. Statistical Methods for Agricultural Workers (2nd Edn.), Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi.
WHO [World Health Organization], 1996. Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, l2, Australia.
Zabalawy, El., M. Kh., Abou-Shleel, M. S. and Abdel- Kareem, S. M., 2015. Effect of marine on bio-accumulation of heavy metals from polluted soil by some leafy vegetables. Nature and Science, 13(3), 109-116.
Zhao, L., Zhong, S., Fang, K., Qian, Z. and Chen, J., 2012. Determination of cadmium (II), cobalt (II), nickel (II), lead (II), zinc (II), and copper (II) in water samples using dual-cloud point extraction and inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometry. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 239, 206-212.